We will discuss Solar Panel Power Generation Efficiency and the role Solar Trackers can play in improving it. The trackers discussed here are purpose built for Portable Solar Panels. But the underlying science holds true for all Solar Panels. For purposes of this blog, Solar Panel are constructed from flexible Monocrystalline Solar Cells (e.g. Maxeon) rated ~23% efficiency.
Types of Solar Panels
A quick summary on popular Solar Panels commercially available today and their characteristics:
Monocrystalline
- Highly Efficient
- Aesthetically pleasing (pure silicon crystal)
- Higher priced
Polycrystalline
- Less Efficient (15-20%)
- Cheaper to produce (silicon fragments)
- Odd looking with bluish hue
Thin Film
- Thin, light and flexible
- Low Efficiency (less than 15%)
- Not suitable for residential rooftop
Photovoltaic Effect
Photovoltaic (PV) effect is the phenomenon that converts solar radiation (sunlight) to electricity. Sunlight is actually photons, carrying varying amount of energy (different wavelengths of the solar spectrum). A Solar Panel is made from many PV (Solar) cells, a semiconductor material. When photons strike a Solar Panel, there are 3 possibilities – reflect, absorb or, pass through. Only the absorbed photons can provide energy to generate electricity.
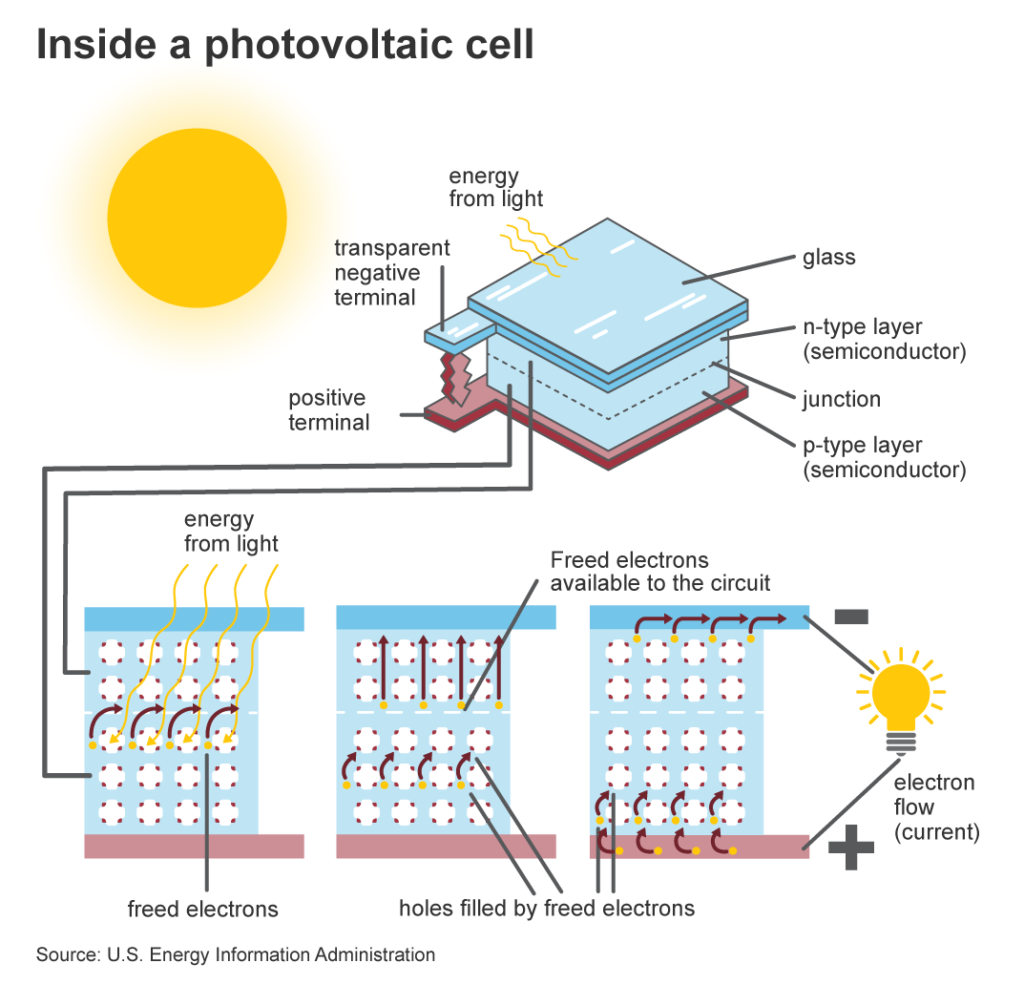
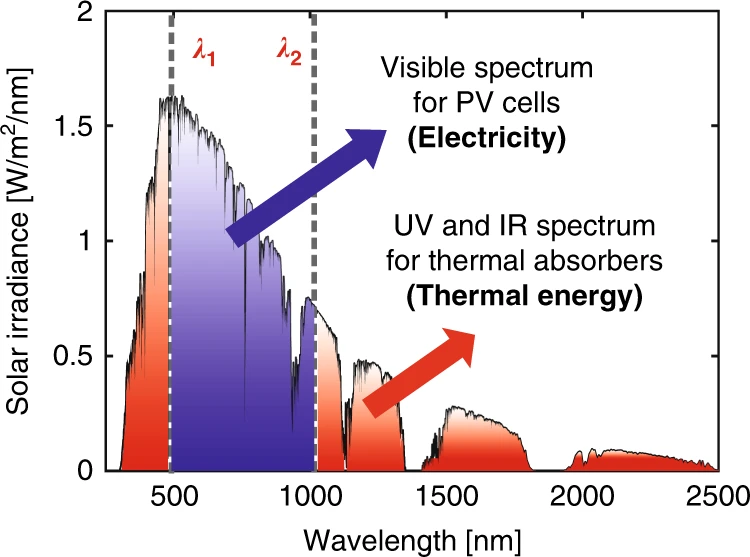
Source: Nature
Usable Solar Energy (for Solar Panels)
Total solar radiation spans from wavelength region 280nm to 4,000nm. About 99% of solar radiation is contained in the wavelength region of ultarviolet (300nm) to near-infrared (3000nm). Reflection is a large source of energy loss in the Earth’s atmosphere. Only wavelength range in 500nm – 1100nm have appropriate energy to excite electrons in the semiconductor material and potentially produce electricity in solar panels when absorbed. All the spectrum losses combined make over 50% of solar radiation unusable for solar power generation.
Additional Reading: NASA visible light
Solar Trackers
A solar panel collects solar radiation more efficiently and hence generates more electricity when the Sun’s rays are perpendicular to the panel. In other words, ideal positioning of a solar panel in relation to the Sun is when the angle of incidence is zero.
Solar Trackers come in 2 flavors:
- Single Axis: These are capable of moving the panel in only a single axis. Adjusting either the Azimuth or, Altitude solar angles.
- Dual Axis: These are capable of moving the panel in 2 axis. Adjusting both the Azimuth and/or, Altitude solar angles.
Dual Axis trackers provide optimal solar panel positioning as they are capable of ensuring a zero angle of incidence throughout the day. This capability comes at an additional cost.
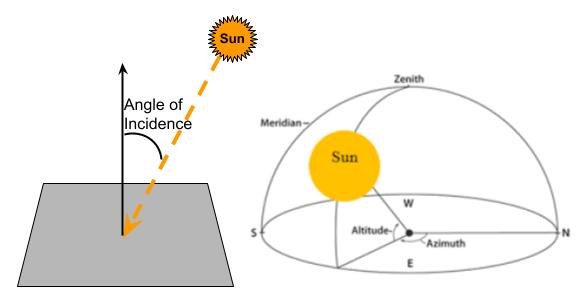
Efficiency Gain from Solar Trackers
Earth’s rotation on its axis and revolution around the Sun means that in relation to a given spot on the Earth (not on the equator), the Solar Path varies for each day of the year. There is a plethora of studies available on the internet that provide both theoretical and measured efficiency gains in power generation when solar panels are mounted on trackers. All these studies assume a fixed installation for a Solar Panel (e.g. on residential rooftops, utility solar farms) since these are the most common use cases. As a reference base case, these studies use a South facing (in Northern Hemisphere) Solar Panel with a fixed tilt (elevation angle). This tilt angle is latitude dependent, higher when closer to the North Pole and smaller when closer to the Equator.
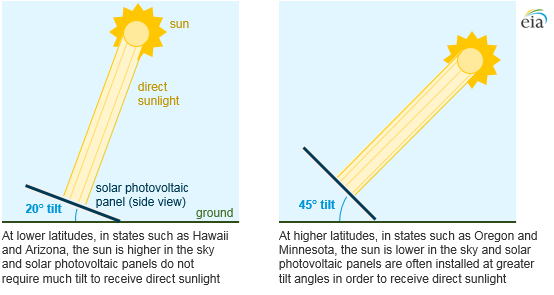
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration
Portable vs. Fixed Panels and Solar Trackers
In our next Blog we will examine the unique requirements and challenges for a Portable Tracker and Solar Panels.